Best Practices For Communication between IND Sponsors and FDA During Drug Development
Purpose
- Describe best practices and procedures for timely, transparent, effective communications between IND sponsors and FDA
- May facilitate earlier availability of safe and effective drugs
Overview
- Philosophy regarding timely interactive communication
- Scope of appropriate interactions
- Types of advice
- General expectations FDA response timing
- Best Practices and Communication Methods
- Formal Meetings
- Written Correspondence from FDA
- Sponsor Submissions
- Acknowledging Receipt of Communications
- Email Between FDA and Sponsors
- General Telephone Calls Between FDA and Sponsors
- Faxes Between FDA and Sponsors
- Use of Out-of-Office Messages by FDA and Sponsors
Resources for Sponsors
- Guidances, Policy and Procedures, Basics for Industry, Interactive Media, Presentations, Labeling and Approvals, Rules and Regulations, Scientific Research Results, Code of Federal Regulations
Additional Contacts
- CDER : Biomarker Qualification Program, Controlled Substance Staff , Division of Drug Information, Division of Pediatric and Maternal Health, Emerging Technology Team, Enhanced Communication Team, Import/Export, Office of Pharmaceutical Quality, Ombudsman, Rare Diseases Program, Small Business and Industry Assistance Program, Therapeutic Biologics and Biosimilars Staff
- CBER : Manufacturers Assistance and Technical Training, Ombudsman
- Office of Special Medical Programs: Advisory Committee Oversight and Management Staff, Office of Combination Products, Office of Good Clinical Practice, Office of Orphan Products Development, Office of Pediatric Therapeutics

Formal Meetings Between FDA ad Sponsors or Applicants of PDUFA Products
Purpose
- Discuss principles of good meeting management practices (GMMPs)
- Describe standardized procedures for requesting, preparing, scheduling, conducting, documenting formal meetings
Scope
- Meeting Types : Type A, Type B Meeting, Type B (EOP), Type C
- Meeting Formats
- Meeting Requests
- Assessing and Responding to meeting requests: Denied, Granted
- Meeting Package: Submission timing, Copies, Content
- Preliminary Responses
- Rescheduling and Canceling
- Meeting Conduct
- Meeting Minutes

Medical Device Accessories – Describing Accessories and Classification Pathways
Purpose
- Describe policy concerning classification of accessories
- Application of policy to devices that are commonly used as accessorie
- Explain what devices considered an “accessory”
- Describes processes to allow requests for risk- and regulatory control-based classification
Definitions
- Accessory: Finished device intended to support, supplement, and/or augment the
performance of one or more parent devices - Component: [A]ny raw material, substance, piece, part, software, firmware, labeling, or assembly which is intended to be included as part of finished,
packaged, and labeled device - Finished Device: [A]ny device or accessory to any device that is suitable for
use or capable of functioning, whether or not it is packaged, labeled, or sterilized - Parent Device: Finished device whose performance is supported, supplemented, and/or augmented by one or more accessories
Accessory Classification Policy
- Is the article an accessory?
- Supports : Performance of parent device by enabling or facilitating performance according to its intended use
- Supplements: Performance of parent device if it adds new function or new way of using the parent device, without changing intended use
- Augments: Performance of parent device by enabling more safe or effective use
- What are risks of accessory when used as intended with the parent device(s)
- What regulatory controls necessary to provide reasonable assurance of safety
and effectiveness
Accessory Classification Process
- Accessory Requests
- Classification of New Accessory Types through the De Novo Process

Purpose
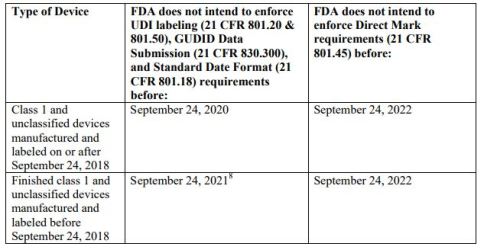
- Describe enforcement of Unique Device Identification (UDI) System
- For Class I and unclassified devices other than implantable, life-supporting or life-sustaining (I/LS/LS) devices
- Does not intend to enforce standard date formatting, labeling, and GUDID data submission requirements
- Does not intend to enforce direct mark requirements
Compliance Dates