FDA BRIEF: Week of August 28, 2017

KYMRIAH (tisagenlecleucel) suspension for intravenous infusion
Novartis
REGULATORY PATHWAY
INDICATION: CD19-directed genetically modified autologous T cell immunotherapy indicated for the treatment of patients up to 25 years of age with B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) that is refractory or in second or later relapse
ADDRESSING UNMET NEED:
- First gene therapy available in the US
- New approach to treatment of cancer and other serious and life-threatening diseases
- New treatment option where very limited options existed, with promising remission and survival rates in clinical trials
REG PATHWAY: BLA
- Priority Review and Breakthrough Therapy designations
- Coordinated, cross-agency approach
- Clinical review : Oncology Center of Excellence
- All other review aspects and final product approval determination: CBER
MECHANISM OF ACTION: CD19-directed genetically modified autologous T cell immunotherapy which involves reprogramming patient’s own T cells with a transgene encoding a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) to identify and eliminate CD19-expressing malignant and normal cells. Upon binding to CD19-expressing cells, CAR transmits a signal to promote T-cell expansion, activation, target cell elimination, and persistence of the KYMRIAH cells.
EFFICACY:
- Open-label, multicenter single-arm trial, n=107, pediatric and young adults with R/R B-cell precursor ALL, lymphodepleting chemotherapy followed by a single dose of KYMRIAH
- Endpoints: Complete Remission (CR) within 3 mo., CR duration, proportion of patients with CR and minimal residual disease (MRD) <0.01% by flow cytometry (MRD-negative)
 SAFETY:
SAFETY:
- Boxed Warning: Cytokine release syndrome (CRS) causing high fever and flu-like symptoms, and for neurological events
- Severe side effects: Serious infections, hypotension, acute kidney injury, fever, hypoxia
- Destruction of normal B cells that produce antibodies – increased risk of infections for a prolonged period of time
REIMBURSEMENT PATHWAY:
- Modernization of current healthcare payment systems need to ensure access to new high-cost therapies
- Innovative payment arrangements including outcome-based pricing in relation to clinical outcomes
- Center for Medicare and Medicaid Innovation (CMMI) to test payment and service delivery models on value-based payment arrangements
- Issue guidance on sponsor engagement in innovative payment arrangements
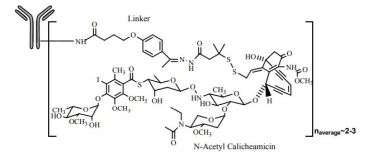 MYLOTARG (gemtuzumab ozogamicin) injection
MYLOTARG (gemtuzumab ozogamicin) injection
Pfizer
INDICATION:
- Newly-Diagnosed CD33-positive Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML): Treatment of newly-diagnosed CD33-positive acute myeloid leukemia in adults
- Relapsed or Refractory CD33-positive AML: Treatment of relapsed or refractory CD33-positive acute myeloid leukemia in adults and in pediatric patients 2 years and older
ADDRESSING UNMET NEED:
- AML is rapidly progressing cancer, forms in bone marrow, results in increased white blood cell
- ~21,380 diagnosed this year in US, 10,590 will die of disease
- Importance of examining alternative dosing, scheduling, and administration of therapies
REG PATHWAY: BLA, Orphan Drug Designation
- Accelerated Approval in 2000 at higher dose for stand-alone treatment for older patients with CD33-positive AML who had experienced a relapse
- Voluntary withdrawal in 2010 after confirmatory trial failed to show clinical benefit and higher rate of fatal toxicity
- This approval includes a lower recommended dose, a different schedule in combination with chemotherapy or on its own, and a new patient population
MECHANISM OF ACTION: CD33-directed antibody-drug conjugate (ADC), small molecule N-acetyl gamma calicheamicin, is a cytotoxic agent covalently attached to antibody. Activity due to binding of ADC to CD33-expressing tumor cells, internalization of ADC-CD33 complex, intracellular release of small molecule
EFFICACY:
- Two, separate trials
- First trial: newly diagnosed AML, n=237, MYLOTARG vs. best supportive care
- Median Overall Survival: 4.9 months vs. 3.6 months
- Second trial: Single-arm study, CD33-positive AML, n=57, single course of MYLOTARG
- Complete Remission. 26% that lasted a median 11.6 months
SAFETY:
- Boxed Warning: Hepatotoxicity, veno-occlusive disease or sinusoidal obstruction syndrome
- Severe side effects: Low blood counts, infections, liver damage, hepatic veno-occlusive disease, infusion-related reactions, hemorrhage
- Common side effects: Pyrexia, nausea, infection, vomiting, bleeding, thrombocytopenia, stomatitis, constipation, rash, headache, elevated liver function tests, neutropenia

VABOMERE™ (meropenem and vaborbactam) for injection
Rempex Pharmaceuticals (The Medicines Company)
INDICATION: Treatment of patients 18 years of age and older with complicated urinary tract infections (cUTI) including pyelonephritis caused by the following susceptible microorganisms: Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, and Enterobacter cloacae species complex
ADDRESSING UNMET NEED:
- Antibacterial product to treat serious or life-threatening infections
- Additional treatment option for patients with cUTI
REG PATHWAY: NDA, Priority Review
- Designated as a qualified infectious disease product (QIDP) under Generating Antibiotic Incentives Now (GAIN)
- Postmarketing Requirements/Commitments: Surveillance study for drug resistance, extractable/leachable studies
MECHANISM OF ACTION: Penem antibacterial drug that inhibits cell wall synthesis in most gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria
EFFICACY:
- Double-blind, double dummy, multi-center trial, N=545 adults with cUTI, including pyelonephritis, VABOMERE vs. piperacillin/tazobactam
- Clinical and microbiological response at the end of IV treatment (EOIVT): Clinical outcome of cure or improvement + microbiologic outcome of eradication
- Clinical and microbiological response at Test of Cure (TOC) visit at 7 d
- Cure/improvement in symptoms + negative urine culture test: 98% vs 94%
- TOC with resolved symptoms + negative urine culture: 77% vs 73%
SAFETY:
- Most common adverse reactions: Headache, infusion site reactions and diarrhea
- Serious risks : Allergic reactions, seizures

BENZNIDAZOLE tablets, for oral use
Exeltis USA
INDICATION: Indicated in pediatric patients 2 to 12 years of age for the treatment of Chagas disease (American trypanosomiasis) caused by Trypanosoma cruzi
ADDRESSING UNMET NEED:
- First approved treatment approved in US
- There may be ~ 300,000 US patients
- Granted tropical disease priority review voucher under section 524 of FDCA
- Voucher entitles designation of a human drug/biologic application as qualifying for a priority review
- Accelerated Approval: Based on negative Immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibody test
- Accelerated Approval Requirement: Prospective, single-arm, multicenter trial, with historical controls, to evaluate safety, efficacy and pharmacokinetics in children
- Postmarketing Requirements: ADME study, Fertility toxicity study
MECHANISM OF ACTION: Inhibits synthesis of DNA, RNA, and proteins within parasite
EFFICACY:
- Two adequate and well-controlled trials
- Trial 1 (Argentina): Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial, children 6-12 yr with chronic indeterminate Chagas disease, n=106, benznidazole vs placebo, followed for 4 years
- Trial 2 (Brazil): Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial, children 7 -12 yr with chronic indeterminate Chagas disease, n=129, benznidazole vs placebo
- Endpoint: Antibodies measured by conventional and nonconventional assays
- Benznidazole treatment resulted in significantly higher percentage of seronegative patients: 55-60% vs 5-14%
SAFETY:
- Most common adverse reactions: Stomach pain, rash, decreased weight, headache, nausea, vomiting, abnormal white blood cell count, urticaria, pruritus, decreased appetite
- Serious risks: Serious skin reactions, nervous system effects and bone marrow depression
- Based on animal findings: Could cause fetal harm when administered to pregnant woman
Image credits: FDA, CDC, Pfizer, Medicines Company